Efek Suhu dan Injeksi Udara pada Penyisihan Limbah Pewarna Tekstil Remazol Red dengan Metode Elektrolisis Plasma
Abstract
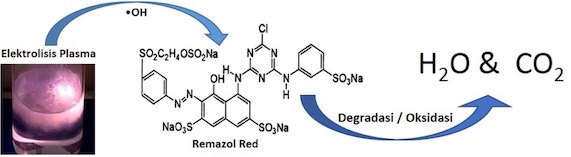
Abstrak. Limbah pewarna industri tekstil merupakan limbah cair yang sulit teroksidasi dan berbahaya bagi lingkungan. Radikal hidroksil (•OH) merupakan spesies yang sangat efektif dalam mengoksidasi berbagai limbah cair organik seperti limbah pewarna. Metode Elektrolisis Plasma sangat produktif menghasilkan radikal Hidroksil sehingga efektif dalam menyisihkan (mendegradasi) berbagai jenis limbah pewarna tekstil seperti Remazol Red. Penelitian ini bertujuan mengoptimalkan proses degradasi remazol red RB 133 dan konsumsi energinya menggunakan metode Elektrolisis Plasma melalui pengaturan suhu dan injeksi gelembung udara dalam larutan. Pembentukan H2O2 merupakan indikator pembentukan •OH pada reaksi Elektrolisis Plasma. Injeksi udara pada larutan limbah pewarna menurunkan arus listrik pada kurva karekateristik arus-tegangan. Kenaikan suhu larutan dari 45 oC menjadi 75 oC selama 10 menit reaksi tampa injeksi udara menurunkan konsumsi energi dari 229,9 kJ menjadi 219,5 kJ serta menurunkan produksi H2O2 dari 4,8 mmol menjadi 3,1 mmol. Sementara injeksi udara pada suhu 75 oC selama 10 menit proses menurunkan konsumsi listrik hingga 28,5% dan meningkatkan produksi H2O2 hingga 27,3 %. Namun demikian injeksi udara hanya meningkatkan degradasi Remazol Red sebesar 1,8 %. Suhu optimum dicapai pada 55oC, dengan produksi H2O2 sebesar 5,7 mmol selama 30 menit. Injeksi udara udara mampu meningkatkan efektivitas proses. Hasil penelitian menunjukkan persen penyisihan mencapai 88,9% dengan konsumsi energi sebesar 115,2 kJ dalam waktu 30 menit reaksi.
Kata kunci: elektrolisis plasma, remazol red, gelembung udara.
Abstract. Effect of Temperature and Air Injection on Degradation of Remazol Red Textile Dyes by Plasma Electrolysis Method. The textile dye waste is a liquid waste that is difficult to oxidize and dangerous for the environment. Hydroxyl radicals (• OH) are very effective species in oxidizing various organic liquid wastes such as Remazol Red. Plasma Electrolysis Method is very productive in producing Hydroxyl radicals, resulting in effective degradation of various types of textile dye waste such as Remazol Red. This study aims to optimize the degradation process of remazol red RB 133 and its energy consumption using the Plasma Electrolysis method through temperature regulation and injection of air bubbles in solution. The formation of H2O2 is used an indicator of the formation of •OH in the Plasma Electrolysis reaction. The Air injection decreases the electric current on the current-voltage characteristic curve. The solution temperature increases from 45oC to 75oC for 10 minutes reaction without air injection were able to reduce the energy consumption from 229.9 kJ to 219.5 kJ and H2O2 production from 4.8 mmol to 3.1 mmol. Meanwhile, the addition of air injection at 75oC within 10 minutes of reaction were able to reduce electricity consumption by 28.5% and increases H2O2 production by 27.3%. However, the addition of air injection only increased the degradation of Remazol Red by 1.8%. The optimum temperature was reached at 55oC, with H2O2 production of 5.7 mmol for 30 minutes. The addition of air injection has been shown to increase the effectiveness of the process. The results showed degradation percentage reached 88.9% with energy consumption of 115.2 kJ within 30 minutes of reaction.
Keywords: air injection, plasma electrolysis, remazol red.
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Agil, M.; Sutariningsih, E., Dekolorisasi Pewarna Indogosol oleh Bakteri Tanah, Prosiding Symbion (Symposium on Biology Education), Yogyakarta, 27 Agustus, 2016.
Ahmed, M.; Suresh, R.; Keun Yang. J; Choi. S.; Lee, H., Effect of Water Conductivity on the Generation of •OH Radicals in High Frequency Underwater Capillary Discharge. International Journal of Renewable Energy and Environmental Engineering, 2016, 4(3), 28-34.
Augusto, O.; Miyamoto, S., Oxygen Radicals and Related Species. Pantopoulos, K., Schipper, H.M., eds. Principles of Free Radical Biomedicine, Nova Biomedical Press, 2011,Vol 1,pp. 1-22.
Day; Underwood, Analisa Kimia Kuantitatif. Jakarta: Penerbit Erlangga, 2002.
Gao, J.; Guo, X.; Ma, D.; Yang, W., The Role of Fe (II) in the Contact Glow Discharged Electrolysis, Plasma Science and Technology. Plasma Science and Technology, 2007, 9(04), 430-435.
Hassaan, M.; Ell Nemr A.; Madkour F.F., Testing the Advanced Oxidation Proceeeses on the Degradation of Direct Blue 86 Dye in Wastewater. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 2017, 43(1), 11-19.
Jiang, B.; Zheng, J.; Qiu, S.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, Z.; Xue, Q., Review on Electrical Discharge Plasma Technology for Wastewater Remediation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 236, 348-368.
Jin, X.; Wang, X.; Yue, J.; & Cai, Y., The Effect of Electrolysis Constituents on Contact Glow Discharge Electrolysis. Electrochimica Acta, 2010, 56, 925-928.
Jyoti, K.K.; Pandit, A.B., Water Disinfection by Acoustic and Hydrodynamic Cavitation. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 7(3), 201-212.
Khairy, M.; Kamal, B.; Amin, N.H.; Mousa, M.A., Kinetic and Isoterm Studies of Remazol Red Adsorption onto Polyaniline/Cerium Oxide Composites. Journal of Basic and Environmental Sciences 3, 2016, 2016, 123-132.
Lau, Y.; Wong, Y.S.; Teng, T.T.; Morad, N.; Rafatullah, M.; Ong, S.A., Degradation of Cationic and Anionic Dyes in Cagulation–Flocculation Process using Bi-functionalized Silica Hybrid with Aluminum-Ferric as Auxiliary Agent. Journal Royal Society of Chemistry, 2015, 5, 34206–34215.
Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Sun, B.; Zu, X., Aqueous 4-nitrophenol Decomposition and Hydrogen Peroxide Formation Induced by Contact Glow Discharged Electrolysis. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 181(1-3), 1010-1015.
Lu, Q.; Yu, J.; Gao, J.; Yang, W.; Li, Y., Glow‐discharge Electrolysis Plasma Induced Synthesis of Polyvinylpyrrolidone/Acrylic Acid Hydrogel and its Adsorption Properties for Heavy‐metal Ions. Plasma Processes and Polymers, 2011, 8(9), 803-814.
Manurung R.; Hasibuan, R.; Irvan, Perombakan, Zat Warna Azo Reaktif secara Anaerob-Aaerob. Prosiding Jurusan Teknik Kimia Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, 11 Oktober 2004.
Marcucci, M.; Ciardelli, G.; Matteucci, A.; Ranieri, L.; Russo, M., Experimental Campaigns on Textile Wastewater for Reuse by Means of Different Membrane Processes. Desalination, 2002, 149(1), 137-143.
Ogugbue, C.J.; Sawidis T., Bioremediation and Detoxification of Synthetic Wastewater Containing Triarylmethane Dyes by Aeromonas hydrophila Isolated from Industrial Effluent. Biotechnology Research International, 2011, 2011, 1-11.
Ruma; Habib, M.A.; Hosseini, S.H.R.; Sakugawa, T.; Akiyama, H., Treatment of Wastewater by Underwater Discharge in Gas Bubbling Water. International Journal of Renewable Energy and Environmental Engineering, 2015, 03(03), 189-194.
Saksono, N.; Nugraha, I.; Gozan, M.; Bismo, S.; Indonesia, U., Plasma Formation Energi and Hydroxyl Production on Contact Glow Discharged Electrolysis. International Journal of Arts & Sciences, 2014, 07(03), 71-77.
Saksono, N.; Puspita, I.; Sukreni, T., Application of Contact Glow Discharge Electrolysis Method for Degradation of Batik Dye Waste Remazol Red by the Addition of Fe2+ ion. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2017, 1823, 020003.
Saito, G.; Nakasugi, Y.; Akiyama T., Generation of Solution Plasma Over a Large Electrode Surface Area, Journal of Applied Physics, 2015, 118, 023303.
Sastrawidana, I.D.K., Perombakan Air Limbah Tekstil menggunakan Jamur Pendegradasi Kayu Jenis Polyporus sp Teramobil pada Serbuk Gergaji Kayu. Jurnal Bumi Lestari, 2012, 2(02), 382-389.
Sengupta, S.K.; Singh, O.P., Contact Glow Discharge Electrolysis: A Study of Its Onset and Location. Journal of electroanalytical chemistry and interfacial electrochemistry, 1991, 301, 189-197.
Sengupta, S.K, Srivastava, A.K., Singh, R., Contact Glow Discharge Electrolysis: A Study on Its Origin in The Light of The Theory of Hydrodynamic Instabilities in Local Solvent Vaporisation by Joule Heating During Electrolysis. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 1997, 427, 23-27.
Shriram, B.; Kanmani, S., Ozonation of Textile Dyeing Wastewater-A Review. Indian Journal of Environmental Protection, 2014, 2014-15(3), 46-50.
Yazici, E.Y.; Deveci, H., Factor Affecting Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide. Proceedings of The XIIth International Mineral Processing Symposium, Cappadocia- Nevsehir, Cappadocia-Nevsehir, 6-8 October, 2010.
Yamtake, A.; Katayama, H.; Yasuoka, K.; Ishii, S., Purification by Atmospheric DC/Pulsed Plasmas Inside Bubbles in Water. International Journal of Plasma Enviromental Science & Technology, 2007, 1(1), 91-95.
Yasuoka, K.; Sato, K., Development of Repetitive Pulsed Plasmas in Gas Bubbles for Water Treatment. International Journal of Plasma Environment Science and Technology, 2009, 3(1), 22-27.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.5614/jtki.2019.18.1.5
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
Copyright (c) 2019 Jurnal Teknik Kimia Indonesia
Jurnal Teknik Kimia Indonesia (JTKI) published by Asosiasi Pendidikan Tinggi Teknik Kimia Indonesia (APTEKIM)
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.


