Pengaruh Radiasi Microwave dan Perlakuan Asam pada Batubara Peringkat Rendah terhadap Perolehan Biosolubilisasi Menggunakan Neurospora intermedia
Abstract
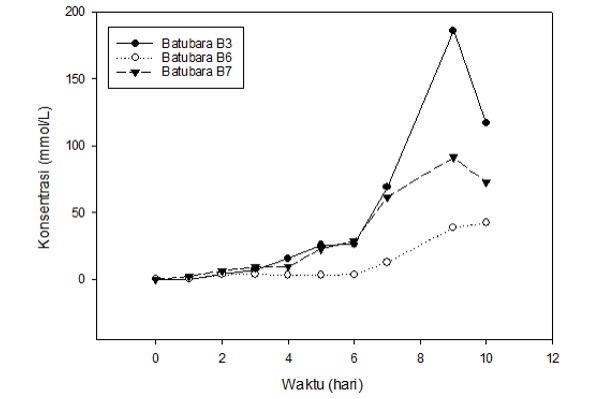
Abstrak. Biosolubilisasi batubara peringkat rendahmerupakan teknologi yang menjanjikan untuk mendapatkan bahan bakar cair yang ramah lingkungan. Biosolubilisasi batubara peringkat rendah dapat dilakukan dengan menggunakan mikroorganisme seperti Neurospora intermedia yang mampu menghasilkan enzim-enzim pensolubilisasi. Mekanisme biosolubilisasibatubaraterjadikarenaadsorpsienzim-enzim tersebutkepermukaan partikel batubara, sehingga proses perlakuan awal batubara perlu dilakukan untuk memudahkan proses adsorpsi enzim.Penelitian ini dilakukan untuk mengkaji pengaruh perlakuan awal partikel batubara peringkat rendah terhadap struktur batubara dan perolehan biosolubilisasi. Pengaruh perlakuan awal tersebut dikaji dengan membandingkan biosolubilisasi menggunakan partikel batubara tanpa perlakuan awal (B1), perlakuan fisik dengan memberikan radiasi microwave 511 Watt selama 5 menit (B2), perlakuan kimiawi dengan merendam partikel batubara dalam HNO3 8 M selama 48 jam (B3), serta perlakuan kombinasi radiasi microwave selama 5 menit dan HNO3 dengan konsentrasi 2, 4, 6, dan 8 M selama 48 jam (B4, B5, B6, dan B7). Partikel batubara B1 memiliki rentang diameter mesopori sebesar 33,97 Å, sedangkan partikel batubara yang telah mengalami perlakuan awal mengalami peningkatan diameter pori namun masih dalam rentang mesopori. Luas permukaan persatuan massa dan volume pori yang tertinggi diperoleh dari perlakuan B3, masing-masing adalah 44,39 m2/g dan 0,09 cc/g. Hasil analisis proksimat dan ultimat menunjukkan bahwa perlakuan asam dapat mengurangi kandungan karbon terikat. Secara kualitatif dapat terlihat bahwa biosolubilisasi batubara B1, B2, B4, dan B5 tidak terjadi dengan baik, sehingga tidak terdapat cairan hitam sebagai hasil batubara yang tersolubilisasi, sedangkan biosolubilisasi batubara B3, B6, dan B7 menghasilkan cairan hitam sejak hari pertama. Secara kuantitatif, biosolubilisasi batubara peringkat rendah menggunakan perlakuan B3 menghasilkan konsentrasi asam humat dan persentase biosolubilisasi yang tertinggi, masing-masing yaitu 186,1 mmol/L dan 67,8%.
Kata kunci: biosolubilisasi batubara, HNO3, Neurospora intermedia, radiasi microwave.
Abstract. Effect of Microwave Radiation and Acid Treatment on Low Grade Coal on Biosolubilization Acquisition Using Neurospora intermedia. Bio-solubilization of low rank coal is a promising technology to obtain environmentally friendly liquid fuel. Bio-solubilization can be carried out using microorganism, such as Neurospora intermedia, which is capable to produce solubilizing enzymes. Mechanism of coal bio-solubilization occurs due to enzymes adsorption onto surface of coal, so that the low rank coal pre-treatment is needed to easy enzyme adsorption. This research examines the effects of low rank coal pre-treatment towards coal structure and bio-solubilization yields. The effects of the pre-treatment were studied by comparing the bio-solubilization using coal with the following specification: without treatment (B1), physical pre-treatment of 511 Watt microwave radiation for 5 minutes (B2), chemical pre-treatment using 8 M HNO3 for 48 hours (B3), and pre-treatment with a combination of microwave radiation for 5 minutes and acid treatment using various HNO3 concentration of 2, 4, 6, and 8 M for 48 hours (B4, B5, B6, and B7, respectively). Coal particle of B1 had mesopore diameter range of 33.97 Å, while coal particle with pre-treatment have increased pore diameter, but are still in range of mesopore. The coal obtained by B3 process has the highest specific surface area and pore volume, which were 44.39 m2/g and 0.99 cc/g, respectively. The proximate and ultimate analyses showed that acid treatment reduced fixed carbon contain. Coal bio-solubilization of B1, B2, B4, and B5 by qualitative could not be solubilized and there was no black liquid as a result of solubilized coal, meanwhile, B3, B6, and B7 were solubilized easily since the first day. Bio-solubilization of chemically pre-treatment low rank coal, B3, resulted in the highest humic acid concentration and bio-solubilization percentage i.e. 186.1 mmol/L and 67.8%, respectively.
Keywords: coal bio-solubilization, HNO3, microwave radiation, Neurospora intermedia.
Keywords
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Alvarez, R.; Clemente, C.; Gomez-Limon, D., The Influence of Nitric Acid Oxidation of Low Rank Coal and Its Impact on Coal Structure. Fuel, 2003, 82, 2007–2015.
Başaran, Y.; Denizli, A.; Sakintuna, B.; Taralp, A.; Yurum, Y., Bio-liquefaction/solubilization of Low-Rank Coal Turkish Lignites and Characterization of The Products. Energy and Fuels, 2003, 17, 1068–1074.
Cohen, M.S.; Gabriele, P.D., Degradation of Coal by the Fungi Polyporus versicolor and Poria monticola. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1982, 44, 23–27.
Delvira, S.; Febriana, K., Effect of Temperature on the Biosolubilization of Low-ranked Coal Using Crude Enzyme from Neurospora sp. Laporan Tugas Akhir Program Sarjana, Institut Teknologi Bandung, Bandung, 2017.
Elbeyli, I.Y.; Pişkin, S., The Effect of Oxidation on The Structure Properties and Calorific Values of Lignites. Sigma, 2004, 4, 43–49.
Hala, A.F.; Fauzan, R.F.S., Pengaruh Jenis Konsentrasi Sumber Karbon Terhadap Biosolubilisasi Batuubara Subbituminous Oleh Neurospora sp. Laporan Tugas Akhir Program Sarjana, Institut Teknologi Bandung, Bandung, 2015.
Hölker, U.; Schmiers, H.; Grosse, S.; Winkelhöfer, M.; Polsakiewicz, M.; Ludwig, S.; Dohse, J.; Höfer, M., Solubilization of Low-rank Coal by Trichoderma atroviride: Evidence for The Involvement of Hydrolytic and Oxidative Enzymes by Using 14C-Labelled Lignite. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2002, 28, 207–212.
Jannah, M., Karakterisasi Produk Biosolubilsasi Batubara Lignit Oleh Kapang Indigenous dari Tanah Pertambangan Sumatera Selatan, Skripsi Program Sarjana, Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah, Jakarta, 2010.
Laborda, F.; Monistrol, I.F.; Luna, N.; Fernandez, M., Processes of Liquefaction/Solubilization of Spanish Coals by Microorganisms. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 1999, 52, 49–56.
Machnikowska, H.; Pawelec, K.; Podgórska, A; Microbial Degradation of Low Rank Coals. Fuel Processing Technology, 2002, 77, 17–23.
Marland, S.; Han, B.; Merchant, A.; Rowson, N., The Effect of Microwave Radiation on Coal Grindability. Fuel, 2000, 79, 1283–1288.
Manoj, B.; Elcey, C.D., Demineralization of Coal by Stepwise Bioleaching: A Study of Sub- bituminous Indian Coal by FTIR and SEM. Journal of the University of Chemical Technology and Metallurgy, 2010, 45, 385–90.
Restiawaty, E.; Arina, L.A.; Budhi, Y.W., Development of Bioethanol Production from Sugarcane Bagasse using Neurospora intermedia on Solid State Culture. Asian Journal of Microbiology, Biotechnology & Environment Sciences, 2018, 20, 98–103.
Sekhohola, L.M.; Igbinigie, E.E.; Cowan, A.K., Biological Degradation and Solubilization of Coal. Biodegradation, 2013, 24, 305–318.
Selvi, A.V.; Banerjee, R.; Ram, L.C.; Singh, G., Biodepolymerization Studies of Low Rank Indian Coals. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2009, 25, 1713-1720.
Shim, J.; Park, S.; Ryu, S., Effect of Modification with HNO3 and NaOH on Metal Adsorption by Pitch-based Activated Carbon Fibers. Carbon, 2001, 39, 1635–1642.
Silva-Stenico, M.E.; Vengadajellum, C.J.; Janjua, H.A.; Harrison, S.T.; Burton, S.G.; Cowan, D.A., Degradation of Low Rank Coal by Trichoderma atroviride ES11. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2007, 34, 625–631.
Sugoro, I.; Hermanto, S.; Indriani. D.; Aditiawati, P.; Sasongko, D., Karakterisasi Produk Biosolubilisasi Batubara oleh kapang T4 Hasil Isolasi dari Tanah Pertambangan Tanjung Enim Sumatera Selatan. Valensi, 2010, 2(1), 325–332.
Sugoro, I.; Astuti, D.I.; Sasongko, D.; Aditiawati, P., Biosolubilisasi Lignit Mentah Hasil Iradiasi Gamma dan oleh Trichoderma asperellum. Jurnal Ilmiah Aplikasi Isotop dan Radiasi, 2012, 8, 51–56.
Tao, X.X.; Pan, L.Y.; Shi, K.Y.; Yin, S.D.; Luo, Z.F., Bio-solubilization of Chinese Lignite I: Extra-cellular Protein Analysis. Mining Science and Technology (China), 2009, 19, 358–362.
Wadhwa, G.; Sharma, D.K., Microbial Pretreatment of Coals: A Tool for Solubilization of Lignite in Organic Solvent–quinoline. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 1998, 14, 751–763.
Yin, S.D.; Tao, X.X.; Shi, K.Y., Bio-solubilization of Chinese Lignite II: Protein Adsorption onto The Lignite Surface. Mining Science and Technology (China), 2009, 19, 363–368.
Yuan, H.L.; Yang, J.S.; Wang, F.Q.; Chen, W.X., Degradation and Solubilization of Chinese Lignite by Penicillium sp. P6. Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology, 2006, 42, 52–55.
Zimmermann, E.; Niemann-Delius, C., Microwave Beneficiation of Brown Coal. Górnictwo i Geoinżynieria, 2007, 31, 627–633.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.5614/jtki.2020.19.1.3
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
Copyright (c) 2020 Jurnal Teknik Kimia Indonesia
Jurnal Teknik Kimia Indonesia (JTKI) published by Asosiasi Pendidikan Tinggi Teknik Kimia Indonesia (APTEKIM)
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.


